News
Explore the Structural Biology of Bioenergy
06/19 
Cells expend much of their effort manipulating the environment around them to their advantage. Doing so takes a lot of energy, for example, to power finding food sources, eating and digesting food molecules, and using these molecules to build new cells. For this reason, cells are masters at harnessing diverse sources of energy and putting them to use. Structural biologists are exploring biomolecules that capture and convert energy in cellular processes. New, advanced techniques are being used to reveal the structure and function of these molecules: continued improvement in the resolution of cryoelectron microscopy is revealing complex and larger protein assemblies involved in bioenergy, and split-second serial crystallography with X-ray free electron lasers is giving a close-up look at rapid energetic transitions.
PDB structures provide insight into the mechanisms and technology of bioenergy.
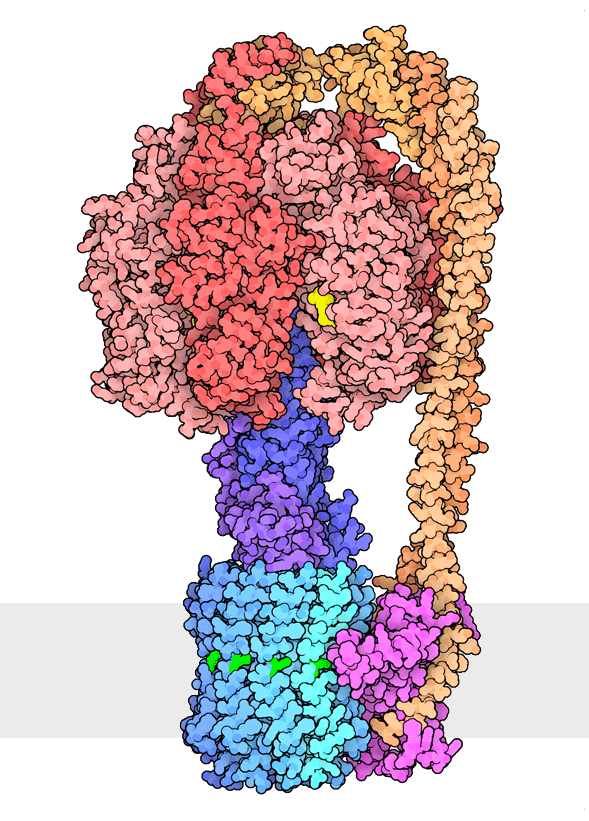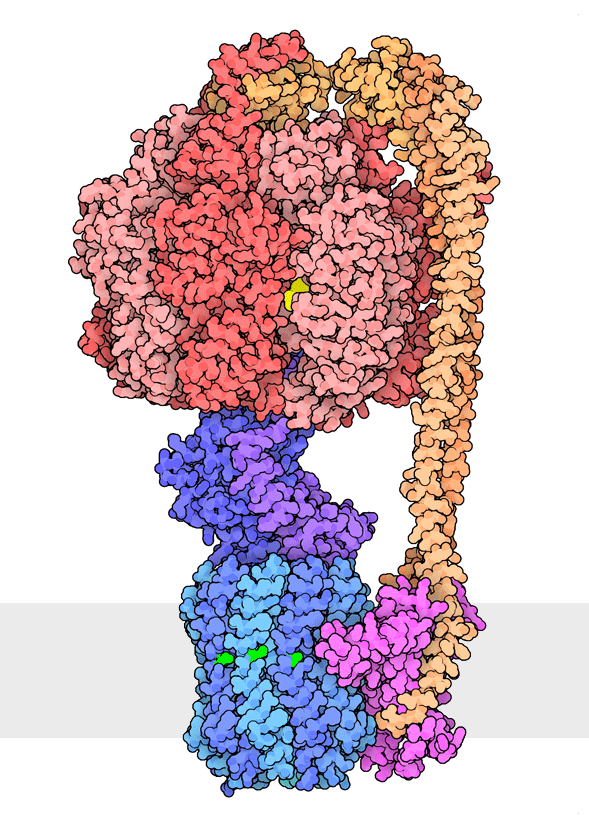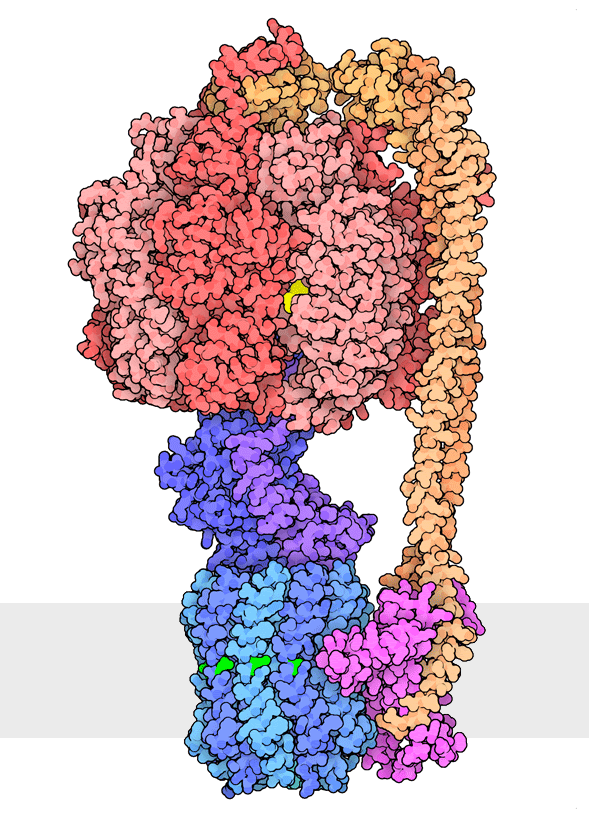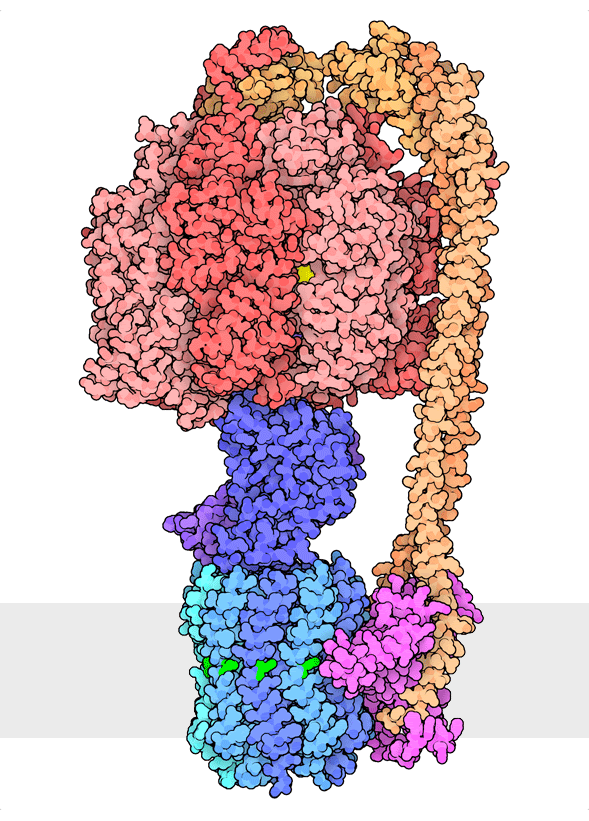 Multiple rotational states of bacterial ATP synthase have been revealed by cryoelectron microscopy. The portion at the top (red) is a rotary motor powered by ATP, and the portion at the bottom is a motor that turns a cylindrical rotor (blue) using the flow of hydrogen ions through a stator subunit (magenta). By connecting these molecular machines together with an asymmetric axle (darker blue at center), one motor can drive the other, using flow of ions to make ATP, or by turning the other direction, using ATP to pump ions.
Multiple rotational states of bacterial ATP synthase have been revealed by cryoelectron microscopy. The portion at the top (red) is a rotary motor powered by ATP, and the portion at the bottom is a motor that turns a cylindrical rotor (blue) using the flow of hydrogen ions through a stator subunit (magenta). By connecting these molecular machines together with an asymmetric axle (darker blue at center), one motor can drive the other, using flow of ions to make ATP, or by turning the other direction, using ATP to pump ions.











